Applies To: Windows Vista,Windows Server 2008
Selects and executes a command on a file or set of files. This command is useful for batch processing.
For examples of how to use this command, see Examples.
Syntax
 Copy Code Copy Code | |
|---|---|
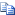
forfiles [/p <Path>] [/m <SearchMask>] [/s] [/c "<Command>"] [/d [{+|-}][{<Date>|<Days>}]] | |
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
/p <Path> |
Specifies the path from which to start the search. By default, searching starts in the current working directory. |
|
/m <SearchMask> |
Searches files according to the specified search mask. The default search mask is *.*. |
|
/s |
Instructs the forfiles command to search into subdirectories recursively. |
|
/c "<Command>" |
Runs the specified command on each file. Command strings should be enclosed in quotation marks. The default command is "cmd /c echo @file". |
|
/d [{+|-}][{<Date>|<Days>}] |
Selects files with a last modified date within the specified time frame.
|
|
/? |
Displays help at the command prompt. |
Remarks
-
Forfiles is most commonly used in batch files.
-
Forfiles /s is similar to dir /s.
-
You can use the following variables in the command string as specified by the /c command-line option.
Variable Description @FILE
File name.
@FNAME
File name without extension.
@EXT
File name extension.
@PATH
Full path of the file.
@RELPATH
Relative path of the file.
@ISDIR
Evaluates to TRUE if a file type is a directory. Otherwise, this variable evaluates to FALSE.
@FSIZE
File size, in bytes.
@FDATE
Last modified date stamp on the file.
@FTIME
Last modified time stamp on the file.
-
With forfiles, you can run a command on or pass arguments to multiple files. For example, you could run the type command on all files in a tree with the .txt file name extension. Or you could execute every batch file (*.bat) on drive C, with the file name "Myinput.txt" as the first argument.
-
With forfiles, you can do any of the following:
-
Select files by an absolute date or a relative date by using the /d parameter.
-
Build an archive tree of files by using variables such as @FSIZE and @FDATE.
-
Differentiate files from directories by using the @ISDIR variable.
-
Include special characters in the command line by using the hexadecimal code for the character, in 0xHH format (for example, 0x09 for a tab).
-
Select files by an absolute date or a relative date by using the /d parameter.
-
Forfiles works by implementing the recurse subdirectories flag on tools that are designed to process only a single file.
Examples
To list all of the batch files on drive C, type:
 Copy Code Copy Code | |
|---|---|
forfiles /p c:\ /s /m *.bat /c "cmd /c echo @file is a batch file" | |
To list all of the directories on drive C, type:
 Copy Code Copy Code | |
|---|---|
forfiles /p c:\ /s /m *.* /c "cmd /c if @isdir==true echo @file is a directory" | |
To list all of the files in the current directory that are at least one year old, type:
 Copy Code Copy Code | |
|---|---|
forfiles /s /m *.* /d -365 /c "cmd /c echo @file is at least one year old." | |
To display the text "File is outdated" for each of the files in the current directory that are older than January 1, 2007, type:
 Copy Code Copy Code | |
|---|---|
forfiles /s /m *.* /d -01/01/2007 /c "cmd /c echo @file is outdated." | |
To list the file name extensions of all the files in the current directory in column format, and add a tab before the extension, type:
 Copy Code Copy Code | |
|---|---|
forfiles /s /m *.* /c "cmd /c echo The extension of @file is 0x09@ext" | |




