Applies To: Windows Server 2008,Windows Vista
Displays information about user sessions on a terminal server.
For examples of how to use this command, see Examples.
Syntax
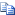 Copy Code Copy Code | |
|---|---|
query user [<UserName> | <SessionName> | <SessionID>] [/server:<ServerName>] | |
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
<UserName> |
Specifies the logon name of the user that you want to query. |
|
<SessionName> |
Specifies the name of the session that you want to query. |
|
<SessionID> |
Specifies the ID of the session that you want to query. |
|
/server:<ServerName> |
Specifies the terminal server that you want to query. Otherwise, the current terminal server is used. |
|
/? |
Displays help at the command prompt. |
Remarks
-
You can use this command to find out if a specific user is logged on to a specific terminal server. Query user returns the following information:
-
The name of the user
-
The name of the session on the terminal server
-
The session ID
-
The state of the session (active or disconnected)
-
The idle time (the number of minutes since the last keystroke or mouse movement at the session)
-
The date and time the user logged on
-
The name of the user
-
To use query user, you must have Full Control permission or Query Information special access permission.
-
If you use query user without specifying <UserName>, <SessionName>, or <SessionID>, a list of all users who are logged on to the server is returned. Alternatively, you can also use query session to display a list of all sessions on a server.
-
When query user returns information, a greater than (>) symbol is displayed before the current session.
-
The /server parameter is required only if you use query user from a remote server.
Examples
-
To display information about all users logged on the system, type:
 Copy Code
Copy Codequery user
-
To display information about the user USER1 on server SERVER1, type:
 Copy Code
Copy Codequery user USER1 /server:SERVER1




